Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Using Inline Functions (Query)#
This example shows you how to use the inline functions in PyMAPDL.
Inline functions like UX have been implemented in PyMAPDL as methods
on the mapdl.inline_functions.Query object. In this example we set
up a simple simulation and use Query to demonstrate some of its
functionality.
First, get an instance of
ansys.mapdl.core.inline_functions.Query below, using the
mapdl property queries.
from ansys.mapdl.core import launch_mapdl
mapdl = launch_mapdl()
# clear at the start and enter the preprocessing routine
mapdl.clear()
mapdl.prep7()
q = mapdl.queries
Setup Mesh#
Assign element type
SOLID5to element type 1Create a cuboid
mapdl.block10 x 20 x 30 in dimensionSet element size to 2
Mesh the block
Plot the elements created
mapdl.et(1, "SOLID5")
mapdl.block(0, 10, 0, 20, 0, 30)
mapdl.esize(2)
mapdl.vmesh("ALL")
mapdl.eplot()
Setup Boundary Conditions#
Assign an Elastic modulus in the x-direction to material 1 of 21e9
And a poisson’s ratio of 0.3
Select all nodes at the
z = 30end of the blockRemove all degrees of freedom for all nodes in the selection
Select all nodes at the
z = 0endApply a x-direction force of 10000 to all of these
Finish preprocessing
mapdl.mp("EX", 1, 210e9)
mapdl.mp("PRXY", 1, 0.3)
mapdl.nsel("S", "LOC", "Z", 30)
mapdl.d("ALL", "UX")
mapdl.d("ALL", "UY")
mapdl.d("ALL", "UZ")
mapdl.nsel("S", "LOC", "Z", 0)
mapdl.f("ALL", "FX", 10000)
mapdl.finish()
***** ROUTINE COMPLETED ***** CP = 0.000
Setup Boundary Conditions#
Enter solution (
mapdl.slashsolualso works)Set the analysis type to
STATICSelect all nodes
Solve the model
Finish solution
mapdl.run("/SOLU")
mapdl.antype("STATIC")
mapdl.allsel()
mapdl.solve()
mapdl.finish(mute=True)
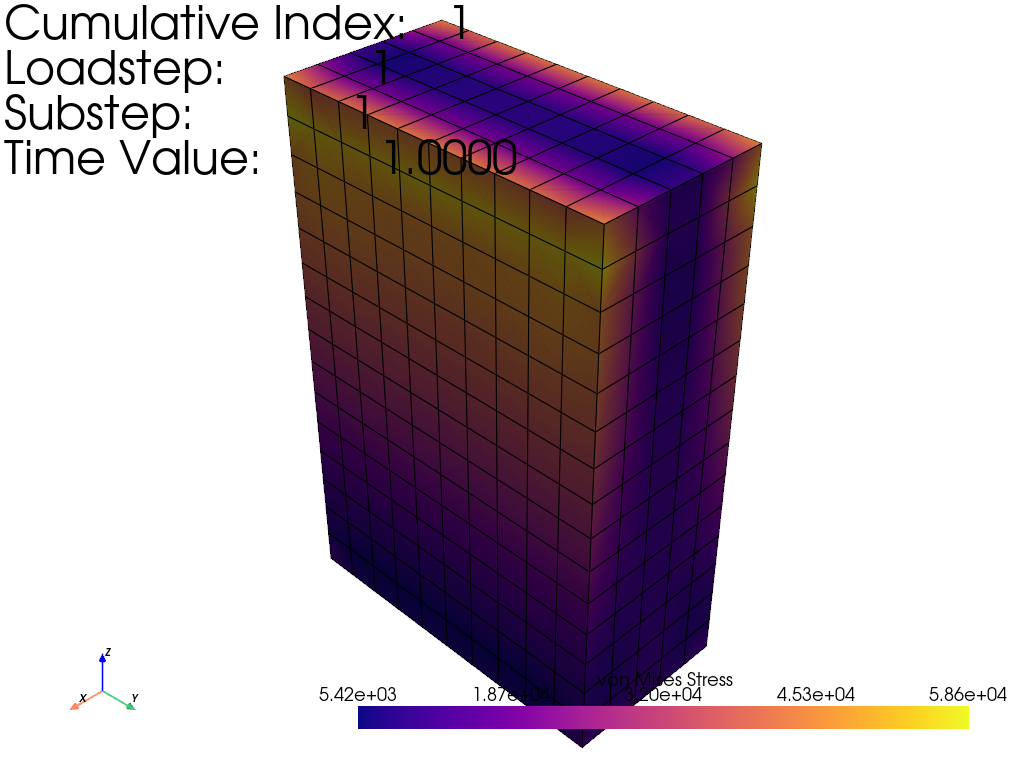
Post-Processing#
Get the result from the
mapdlinstancePlot the equivalent stress results - Show the edges so that we can see the element boundaries - Use the “plasma” colormap because it is perceptually uniform
result = mapdl.result
result.plot_principal_nodal_stress(0, "SEQV", show_edges=True, cmap="plasma")
Using Query#
Use
Queryto get the nodes nearest to (5, 0, 0) and (5, 10, 0)Use the
Queryinstance to examine the x, y, and z displacement.Print the results in a formatted string.
node1 = q.node(5.0, 0.0, 0.0)
node2 = q.node(5.0, 10.0, 0.0)
for node in [node1, node2]:
x_displacement = q.ux(node)
y_displacement = q.uy(node)
z_displacement = q.uz(node)
message = f"""
************************
Displacement at Node {node}:
************************
X | {x_displacement}
Y | {y_displacement}
Z | {z_displacement}
"""
print(message)
************************
Displacement at Node 28:
************************
X | 1.757716378392436e-05
Y | 3.036257546792005e-09
Z | -7.982690758479201e-07
************************
Displacement at Node 48:
************************
X | 1.761241767518258e-05
Y | -3.9107243951258375e-20
Z | -8.070989838528406e-07
Stop mapdl#
mapdl.exit()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.237 seconds)

