Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
MAPDL 3D Beam Example#
This is a simple example that loads an archive file containing a beam
and then runs a modal analysis using the simplified modal_analysis
method.
First, start by launching MAPDL as a service.
from ansys.mapdl.reader import examples
from ansys.mapdl.core import launch_mapdl
mapdl = launch_mapdl()
# load a beam stored as an example archive file and mesh it
mapdl.cdread("db", examples.hexarchivefile)
mapdl.esel("s", "ELEM", vmin=5, vmax=20)
mapdl.cm("ELEM_COMP", "ELEM")
mapdl.nsel("s", "NODE", vmin=5, vmax=20)
mapdl.cm("NODE_COMP", "NODE")
# boundary conditions
mapdl.allsel()
# dummy steel properties
mapdl.prep7()
mapdl.mp("EX", 1, 200e9) # Elastic moduli in Pa (kg/(m*s**2))
mapdl.mp("DENS", 1, 7800) # Density in kg/m3
mapdl.mp("NUXY", 1, 0.3) # Poissons Ratio
mapdl.emodif("ALL", "MAT", 1)
# fix one end of the beam
mapdl.nsel("S", "LOC", "Z")
mapdl.d("all", "all")
mapdl.allsel()
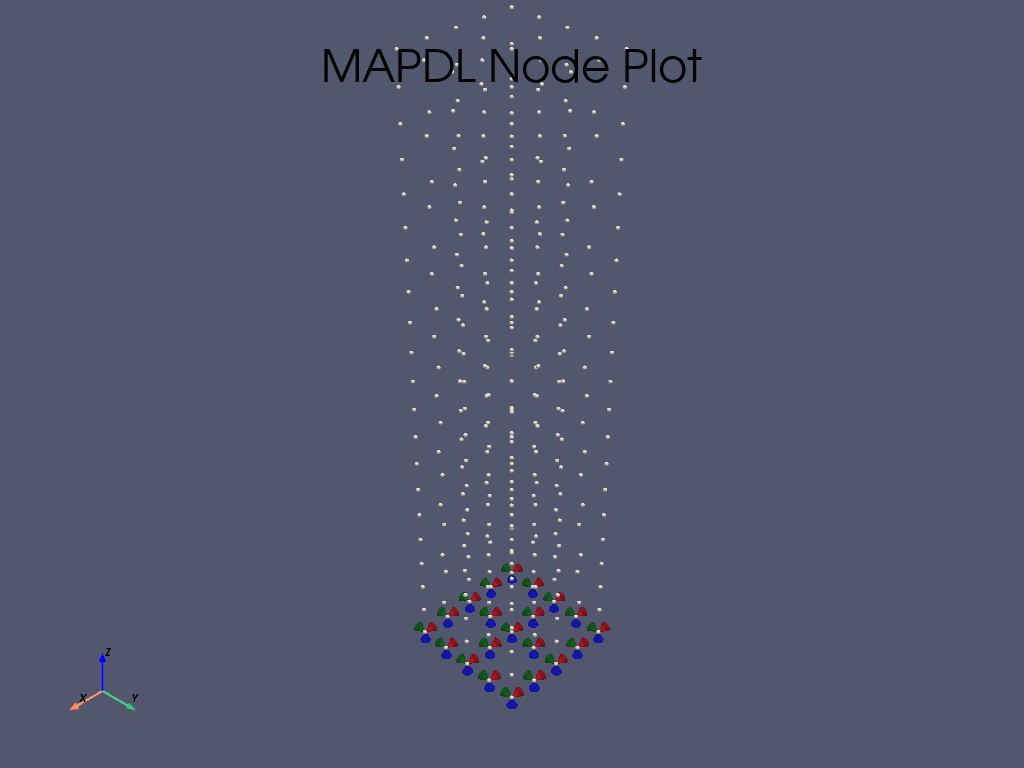
# plot the boundary conditions
mapdl.nplot(plot_bc=True)
mapdl.mxpand(elcalc="YES")
mapdl.modal_analysis(nmode=6)
***** MAPDL SOLVE COMMAND *****
*** NOTE *** CP = 0.000 TIME= 00:00:00
There is no title defined for this analysis.
*** SELECTION OF ELEMENT TECHNOLOGIES FOR APPLICABLE ELEMENTS ***
---GIVE SUGGESTIONS ONLY---
ELEMENT TYPE 1 IS SOLID186. KEYOPT(2) IS ALREADY SET AS SUGGESTED.
*****MAPDL VERIFICATION RUN ONLY*****
DO NOT USE RESULTS FOR PRODUCTION
S O L U T I O N O P T I O N S
PROBLEM DIMENSIONALITY. . . . . . . . . . . . .3-D
DEGREES OF FREEDOM. . . . . . UX UY UZ
ANALYSIS TYPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MODAL
EXTRACTION METHOD. . . . . . . . . . . . . .BLOCK LANCZOS
NUMBER OF MODES TO EXTRACT. . . . . . . . . . . 6
GLOBALLY ASSEMBLED MATRIX . . . . . . . . . . .SYMMETRIC
NUMBER OF MODES TO EXPAND . . . . . . . . . . .ALL
ELEMENT RESULTS CALCULATION . . . . . . . . . .ON
*** NOTE *** CP = 0.000 TIME= 00:00:00
The conditions for direct assembly have been met. No .emat or .erot
files will be produced.
D I S T R I B U T E D D O M A I N D E C O M P O S E R
...Number of elements: 40
...Number of nodes: 321
...Decompose to 0 CPU domains
...Element load balance ratio = 0.000
L O A D S T E P O P T I O N S
LOAD STEP NUMBER. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
THERMAL STRAINS INCLUDED IN THE LOAD VECTOR . . YES
PRINT OUTPUT CONTROLS . . . . . . . . . . . . .NO PRINTOUT
DATABASE OUTPUT CONTROLS. . . . . . . . . . . .ALL DATA WRITTEN
*********** PRECISE MASS SUMMARY ***********
TOTAL RIGID BODY MASS MATRIX ABOUT ORIGIN
Translational mass | Coupled translational/rotational mass
39000. 0.0000 0.0000 | 0.0000 97500. -19500.
0.0000 39000. 0.0000 | -97500. 0.0000 19500.
0.0000 0.0000 39000. | 19500. -19500. 0.0000
------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------
| Rotational mass (inertia)
| 0.33800E+06 -9750.0 -48750.
| -9750.0 0.33800E+06 -48750.
| -48750. -48750. 26000.
TOTAL MASS = 39000.
The mass principal axes coincide with the global Cartesian axes
CENTER OF MASS (X,Y,Z)= 0.50000 0.50000 2.5000
TOTAL INERTIA ABOUT CENTER OF MASS
84500. -0.54570E-11 -0.14552E-10
-0.54570E-11 84500. -0.29104E-10
-0.14552E-10 -0.29104E-10 6500.0
The inertia principal axes coincide with the global Cartesian axes
*** MASS SUMMARY BY ELEMENT TYPE ***
TYPE MASS
1 39000.0
Range of element maximum matrix coefficients in global coordinates
Maximum = 9.116809117E+10 at element 0.
Minimum = 9.116809117E+10 at element 0.
*** ELEMENT MATRIX FORMULATION TIMES
TYPE NUMBER ENAME TOTAL CP AVE CP
1 40 SOLID186 0.000 0.000000
Time at end of element matrix formulation CP = 0.
BLOCK LANCZOS CALCULATION OF UP TO 6 EIGENVECTORS.
NUMBER OF EQUATIONS = 900
MAXIMUM WAVEFRONT = 0
MAXIMUM MODES STORED = 6
MINIMUM EIGENVALUE = 0.00000E+00
MAXIMUM EIGENVALUE = 0.10000E+31
Memory available (MB) = 0.0 , Memory required (MB) = 0.0
*****MAPDL VERIFICATION RUN ONLY*****
DO NOT USE RESULTS FOR PRODUCTION
*** FREQUENCIES FROM BLOCK LANCZOS ITERATION ***
MODE FREQUENCY (HERTZ)
1 32.13951614477
2 32.13951614481
3 145.4783895431
4 173.4557943042
5 173.4557943042
6 254.8511237205
View the results using the pyansys result object
result = mapdl.result
print(result)
PyMAPDL Result
Units : User Defined
Version : 25.2
Cyclic : False
Result Sets : 6
Nodes : 321
Elements : 40
Available Results:
EMS : Miscellaneous summable items (normally includes face pressures)
ENF : Nodal forces
ENS : Nodal stresses
ENG : Element energies and volume
EEL : Nodal elastic strains
ETH : Nodal thermal strains (includes swelling strains)
EUL : Element euler angles
EPT : Nodal temperatures
NSL : Nodal displacements
RF : Nodal reaction forces
Access nodal displacement values
50 [-0.00150879 0.00187603 0.00138844]
51 [-0.00183577 0.00228864 0.0014931 ]
52 [-0.00218401 0.00272783 0.00158312]
53 [-0.00255026 0.00318949 0.00165894]
54 [-0.00293143 0.00366976 0.00172149]
55 [-0.00332458 0.0041649 0.00177153]
56 [-0.00372703 0.00467155 0.00181027]
57 [-0.00413627 0.00518652 0.0018387 ]
58 [-0.00455017 0.00570713 0.00185832]
59 [-0.00496678 0.00623092 0.00187037]
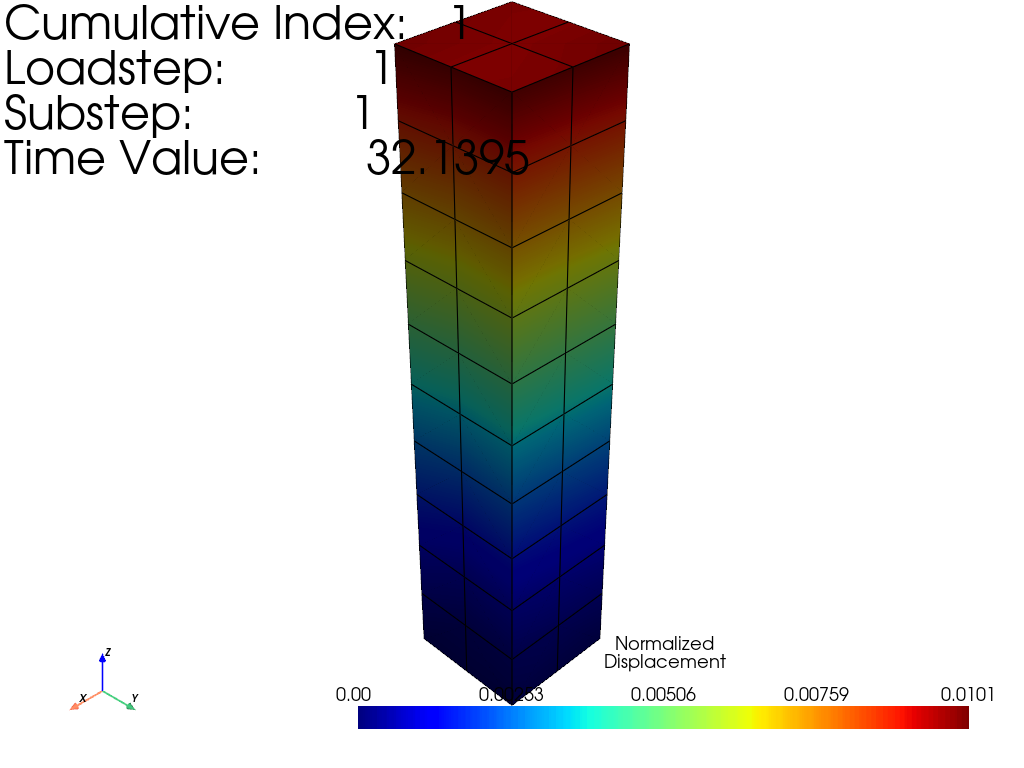
Plot a modal result
result.plot_nodal_displacement(0, show_edges=True)
Animate a modal result result.animate_nodal_solution(0, show_edges=True, loop=False, displacement_factor=10, movie_filename=’demo.gif’)
Stop mapdl#
mapdl.exit()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.089 seconds)

